It’s easy to overlook one of the most important aspects of our well-being: mental health. Often, we tend to prioritize our physical health, but mental health is just as critical for a balanced and fulfilling life.
Exercise, however, is one powerful tool that can improve both physical and mental health. While many people associate regular exercise with weight loss, increased stamina, or physical strength, its impact on mental health cannot be underestimated. At Active Health Sport, we believe in the comprehensive benefits of regular exercise. In this blog, we’ll explore the various ways regular physical activity can improve mental health, boost mood, reduce stress, and contribute to a healthier and more positive outlook on life.
Stress is an inevitable part of life. Whether it’s the pressure from work, family demands, or simply the day-to-day challenges that come with modern living, everyone experiences stress. While occasional stress is a natural response to life’s pressures, chronic stress can hurt both mental and physical health.
It can lead to feelings of anxiety, fatigue, and irritability, and even contribute to more severe health conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and depression. But there is good news: regular exercise can be a powerful and natural tool in reducing and managing stress.
How Does Exercise Help Relieve Stress?
Exercise works as a natural stress reliever by influencing both the body and the mind in positive ways. Here are some of the mechanisms that make physical activity such an effective way to combat stress:
- Reduction in Cortisol Levels
Cortisol is often called the “stress hormone” because the adrenal glands release it in response to stress. High levels of cortisol over prolonged periods can contribute to various health problems, including anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Exercise helps to reduce cortisol levels in the body, which can alleviate the physiological symptoms of stress. This reduction in cortisol allows the body to return to a state of balance, making it easier to manage stress. - Endorphin Release – The “Feel-Good” Hormones
Physical activity triggers the production of endorphins, the body’s natural mood enhancers. These chemicals act as natural painkillers and mood boosters. When endorphins are released during exercise, they create a sense of euphoria and relaxation, often referred to as a “runner’s high.” This mood boost is an immediate response to physical activity, helping to counteract the feelings of tension and anxiety caused by stress. - Improved Sleep Quality
Stress often affects sleep, leading to insomnia or restless nights. This lack of quality sleep can, in turn, exacerbate stress and anxiety. Regular exercise improves sleep patterns, helping you fall asleep more quickly and experience deeper, more restorative sleep. Better sleep improves your ability to cope with stress the following day and ensures your body and mind have time to recharge and recover. - Distraction from Stressors
Exercise provides a healthy and productive distraction from the stressors in your life. When you engage in physical activity, you focus your attention on the movement of your body, the rhythm of your breathing, or the goal you’re working toward. This distraction from your worries can give your mind a break from stress, allowing you to return to your challenges with a clearer, more focused perspective. - Improved Mood and Self-Confidence
As you engage in regular physical activity, you begin to see improvements in your overall fitness level, strength, and endurance. This sense of accomplishment can contribute to increased self-esteem and confidence, which can help reduce stress. Knowing that you’re taking steps to take care of your body and mind provides a sense of empowerment that makes it easier to manage stressful situations. - Social Interaction
Exercise often provides opportunities for social engagement, whether through group fitness classes, sports, or even casual walks with friends. Socializing during physical activity can act as an important outlet for stress. The support and camaraderie of others can make challenges feel more manageable and provide a sense of connection that counters the feelings of isolation that stress can sometimes create. - Mindfulness and Relaxation
Certain types of exercise, such as yoga or Tai Chi, focus on slow, controlled movements and deep breathing techniques. These exercises promote mindfulness and relaxation, helping you to become more aware of your body and your breath while also calming your mind. Engaging in these activities can teach you how to better handle stressful situations by promoting a sense of calm and mindfulness during moments of tension.
Types of Exercise that Help Relieve Stress
The great thing about exercise is that it can come in many forms, and almost any type of physical activity can help reduce stress. Some exercises, however, are particularly effective in providing mental relief. Here are a few examples:
- Aerobic Exercise (Running, Cycling, Swimming)
Aerobic exercises are great for increasing heart rate and improving overall cardiovascular health. Activities like running, cycling, and swimming stimulate the release of endorphins, which help to improve mood and reduce stress. These exercises also require a level of focus and effort that can provide a mental distraction from your worries. - Strength Training (Weightlifting, Resistance Training)
Strength training builds muscle and improves body strength, but it also has mental benefits. The act of lifting weights and setting fitness goals helps boost confidence and provides a sense of achievement. Additionally, the mental focus required during a strength training session can help clear your mind and provide relief from stress. - Yoga
Yoga combines movement, breathwork, and mindfulness. The deep breathing involved in yoga helps to activate the parasympathetic nervous system (the body’s relaxation response), counteracting the effects of stress. Many people find yoga to be an effective way to reduce mental tension, improve flexibility, and restore inner peace. - Mindfulness Practices (Tai Chi, Pilates)
Like yoga, activities such as Tai Chi and Pilates focus on mindful movement and breathing. These practices have been shown to help reduce stress, improve mental clarity, and promote overall well-being. The meditative aspect of these exercises makes them ideal for reducing the physiological and psychological impacts of stress. - Walking or Hiking in Nature
Simply taking a walk, especially in a natural setting like a park or hiking trail, can significantly reduce stress levels. Being in nature allows you to disconnect from daily worries and recalibrate your mind. Walking or hiking provides a low-impact exercise that can help to clear your head and rejuvenate your spirit.
Making Exercise Part of Your Stress-Relief Routine
Incorporating exercise into your daily or weekly routine doesn’t have to be complicated or time-consuming. Even small amounts of physical activity can have a positive impact on stress levels. Here are a few tips for making exercise a regular part of your stress-relief plan:
- Start Small and Gradually Build Up
If you’re new to exercise or haven’t been active in a while, start with shorter sessions. Begin with a 15-minute walk or a gentle yoga session, and gradually increase the duration and intensity as you feel more comfortable. - Find Activities You Enjoy
Exercise doesn’t have to feel like a chore. Choose activities that you find enjoyable, whether that’s dancing, cycling, swimming, or even playing a sport. The more you enjoy your workout, the more likely you are to stick with it and use it as a regular stress reliever. - Consistency is Key
To reap the stress-relieving benefits of exercise, consistency is important. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. This could be spread throughout the day, whether it’s a brisk walk during lunch or a workout after work. The key is making physical activity a regular part of your routine. - Use Exercise as a Break
When life gets overwhelming, exercise can provide a much-needed break. Step away from your daily tasks, whether it’s work or household chores, and use that time to engage in physical activity. A break from stressors allows you to return to them with a fresh perspective and a calmer mind. - Set Goals
Setting realistic fitness goals can provide you with a sense of purpose and motivation. Whether it’s aiming to walk 10,000 steps a day or mastering a new yoga pose, having clear objectives can keep you focused and help you stay on track, making exercise even more rewarding.
Also Read the Latest: Is Walking 10000 Steps Enough for Your Health Goals?
2. Exercise Reduces Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety
Depression and anxiety are among the most widespread mental health challenges in the world today. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 300 million people worldwide suffer from depression, and anxiety disorders affect even more. These conditions can severely affect daily life, impacting work, relationships, and overall well-being.
Traditional treatment methods, such as therapy and medication, are often effective for managing these conditions. However, incorporating regular exercise into your lifestyle can offer a valuable supplementary approach that addresses both the body and the mind.
How Does Exercise Help Combat Depression and Anxiety?
The connection between exercise and mental health can be traced back to the way physical activity influences brain chemistry. Exercise is a powerful tool for mental health, not only because it provides physical benefits but also because it triggers significant changes in the brain that can alleviate feelings of sadness, anxiety, and despair.
1. Boosting Neurotransmitters:
One of the most direct ways that exercise combats depression and anxiety is by enhancing the production of neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly serotonin and dopamine. These chemicals are often referred to as the “feel-good” chemicals because they help regulate mood, emotions, and behavior.
- Serotonin: This neurotransmitter plays a critical role in stabilizing mood and promoting feelings of well-being. Low levels of serotonin are associated with symptoms of depression, including feelings of hopelessness and sadness. Regular physical activity has been shown to boost serotonin levels in the brain, which can help alleviate these symptoms and promote a more positive outlook on life.
- Dopamine: Dopamine is another key neurotransmitter linked to pleasure, motivation, and reward. It is the brain’s “motivation molecule.” When you exercise, your body releases dopamine, which can help reduce feelings of anxiety, provide a sense of achievement, and give you a more energetic and optimistic view of the world.
2. Reducing Cortisol Levels:
Another way exercise helps reduce anxiety and depression is by lowering cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone. When you’re under stress, your body releases cortisol, which prepares you for a “fight or flight” response. However, prolonged periods of high cortisol levels can lead to feelings of anxiety, increased heart rate, disturbed sleep, and even memory problems.
Regular exercise helps to regulate cortisol levels by allowing the body to release this hormone in controlled bursts during physical exertion. Once the workout is completed, cortisol levels drop, promoting a sense of calm and relaxation. Over time, regular exercise can lead to lower baseline cortisol levels, resulting in less overall anxiety and a better ability to cope with stress.
3. Creating a Sense of Accomplishment:
Exercise also provides a powerful psychological benefit: it fosters a sense of accomplishment. Achieving small fitness goals, such as running a certain distance, lifting a specific weight, or completing a challenging workout, can provide a tremendous boost to self-esteem and confidence. This sense of accomplishment is especially important for individuals who may be struggling with feelings of worthlessness or helplessness that often accompany depression.
For people dealing with anxiety, exercise offers a healthy way to manage and cope with those anxious feelings. By sticking to a fitness routine, individuals create a sense of control over their bodies and their lives, which helps reduce anxiety and build resilience.
Also Read the Latest: How to Reap the Physical and Mental Benefits of Hiking
4. Promoting Relaxation and Mindfulness:
Exercise, especially low-impact activities like yoga, swimming, or walking in nature, can serve as a form of mindfulness. Mindfulness is the practice of being present and fully engaged in the moment, without judgment or distraction. For individuals who experience anxiety or depression, the ability to focus solely on the task at hand, whether it’s breathing, running, or stretching, can provide a sense of calm and clarity.
Mindful movement helps individuals distance themselves from the negative thought patterns that often accompany depression and anxiety. During exercise, the brain’s preoccupation with worry or rumination is replaced with a focus on the body’s movements and sensations. This allows individuals to temporarily “shut off” their stress and anxiety, providing a mental break.
5. The Social Connection:
Another key benefit of exercise, particularly when done in a group or social setting, is the opportunity it offers for social interaction. Isolation is a major risk factor for both depression and anxiety, as it can intensify feelings of loneliness and disconnection. Exercise classes, group runs, sports teams, or simply working out with friends can foster a sense of community and belonging, which can help reduce feelings of isolation.
Social connections play a critical role in mental health recovery. The positive interactions and support from others can serve as a buffer against the negative effects of depression and anxiety. Exercise provides a natural, enjoyable way to connect with others, helping to reduce stress and anxiety while promoting a sense of camaraderie and friendship.
6. Long-Term Effects on Mental Health:
While exercise can provide immediate relief from the symptoms of anxiety and depression, its long-term effects are equally significant. Consistent physical activity has been shown to contribute to long-term improvements in mental health. Studies have demonstrated that individuals who engage in regular exercise are less likely to experience recurring episodes of depression and anxiety. The benefits of exercise extend beyond the immediate effects, providing ongoing support for mental well-being.
In fact, research suggests that exercise can be as effective as antidepressant medication for some individuals. In one study, patients who participated in aerobic exercise programs showed similar improvements in mood and anxiety levels as those who were prescribed antidepressant medications.
7. Exercise as a Coping Mechanism:
One of the most powerful ways exercise helps with depression and anxiety is by providing individuals with a healthy outlet to cope with negative emotions. Rather than turning to unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as alcohol or overeating, exercise offers a productive and positive way to release pent-up stress and emotions.
For people who experience anxiety attacks or depressive episodes, a brisk walk, a quick jog, or a few minutes of stretching can help calm the body and mind, reducing the intensity of these emotions. Over time, this can help individuals develop healthier coping strategies, leading to more consistent and effective management of their mental health.
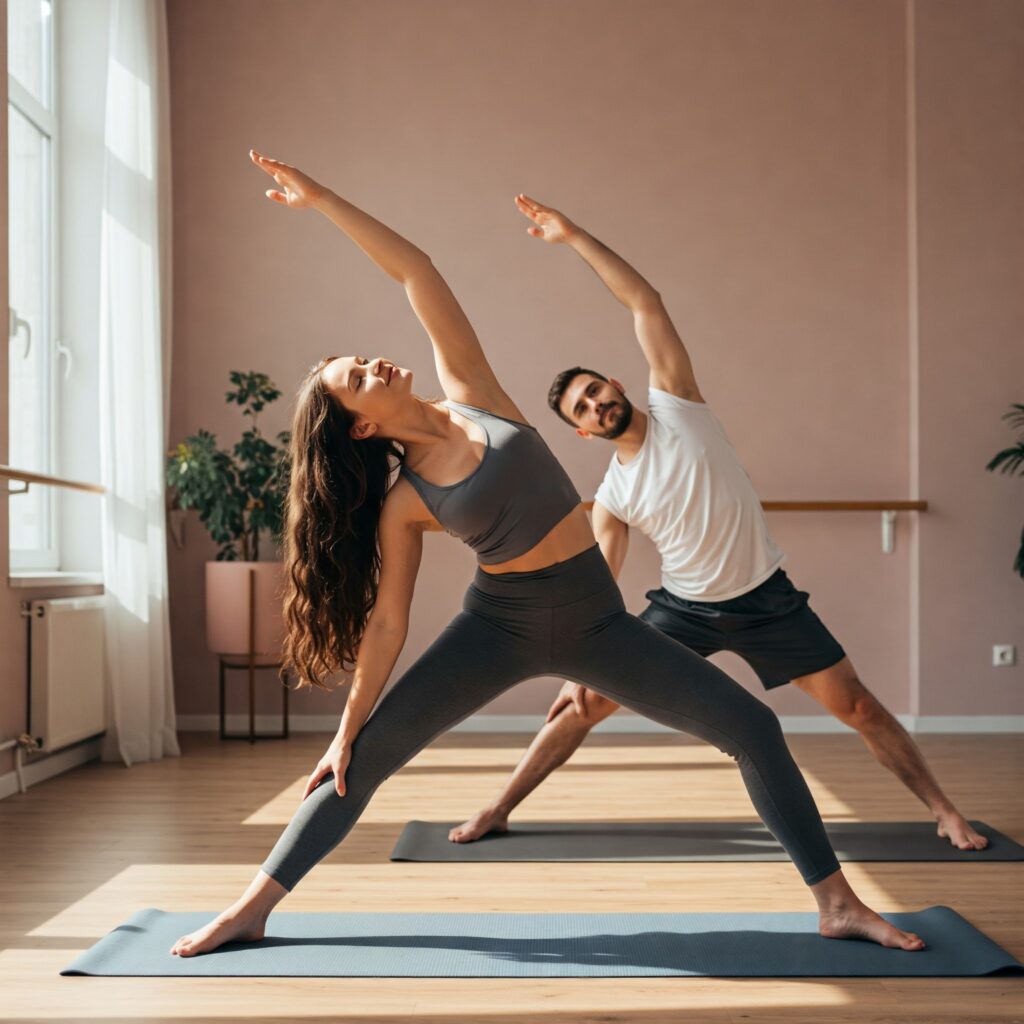

Exercise and Depression | Real-Life Examples
Many individuals have experienced significant improvements in their mental health by incorporating regular exercise into their daily routines. For instance, people who struggle with depression often report feeling “lighter” and more energetic after a few weeks of consistent physical activity. Regular exercise has allowed individuals to rediscover joy in their lives, whether through the endorphin rush after a workout or the sense of pride in achieving a fitness goal.
In a study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, participants who regularly exercised showed a marked reduction in symptoms of depression. Many participants also reported feeling more energized and better able to manage the daily stresses of life.
Additionally, individuals who experience social anxiety often find that group exercise classes or activities like hiking with friends help them feel more comfortable in social settings. This sense of accomplishment and increased social confidence can significantly alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Regular exercise can also improve your self-esteem and overall sense of well-being. When you exercise, you’re taking care of your body, which naturally makes you feel good about yourself. Achieving fitness goals, whether it’s lifting heavier weights, running a faster mile, or simply feeling healthier, provides a boost to your self-confidence.
Why Does Exercise Improve Self-Esteem?
The process of working out helps you develop discipline, resilience, and determination. As you begin to see improvements in your physical health and fitness, it positively influences how you perceive yourself. This, in turn, improves your overall mental well-being.
Exercise can also foster a sense of accomplishment and control. You have the ability to set goals and achieve them, which empowers you and gives you a sense of purpose. This can be especially helpful for individuals dealing with mental health challenges, as it reinforces the belief that they are capable of making positive changes in their lives.
Mental clarity and cognitive function are crucial for both our professional and personal lives. Regular exercise doesn’t just help keep your body in shape, but it also has a profound impact on your brain health. Exercise improves blood flow to the brain, which supports neurogenesis, the process by which new neurons are formed.
How Does Exercise Enhance Cognitive Function?
Physical activity has been linked to improved memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. For example, cardiovascular exercises, like running or cycling, have been shown to increase the size of the hippocampus, the brain region responsible for learning and memory. Additionally, regular exercise helps improve concentration and the ability to make decisions, making it easier to stay focused and productive throughout the day.
Sleep and mental health are closely linked. Poor sleep can contribute to a range of mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and irritability. Conversely, good sleep is essential for mental clarity, emotional stability, and overall well-being. Regular exercise can significantly improve your sleep patterns and quality of rest.
How Does Exercise Promote Better Sleep?
Exercise helps regulate the body’s internal clock, also known as the circadian rhythm. This means that individuals who engage in physical activity tend to fall asleep faster, enjoy deeper sleep, and wake up feeling more rested. Additionally, regular exercise helps reduce feelings of restlessness and anxiety, which often interfere with sleep.
It’s important to note that the timing of your exercise matters. While exercising earlier in the day can promote better sleep, exercising too close to bedtime can have the opposite effect for some people. This is because physical activity increases the heart rate and adrenaline, which may make it harder to fall asleep.
Regular exercise not only improves mental health in the short term but also helps reduce the long-term risk of developing certain mental health disorders. Studies have found that physically active individuals are less likely to develop conditions like depression, anxiety, and even psychotic disorders.
How Does Exercise Lower the Risk of Mental Health Disorders?
Exercise stimulates the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which supports brain health and protects against neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, exercise helps regulate hormones that affect mood and stress levels, ensuring that the brain remains in a balanced state.
Incorporating exercise into your daily routine can serve as a preventive measure, helping to reduce the likelihood of mental health issues arising later in life. By focusing on both physical and mental health, you’re investing in a longer, healthier, and happier future.
For many people, mental health issues can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness. Exercise, particularly group activities or team sports, offers opportunities to meet new people and strengthen social connections. Socializing during exercise can significantly improve mood and foster a sense of belonging.
How Does Social Interaction During Exercise Benefit Mental Health?
When you exercise with others, whether it’s attending a fitness class, playing team sports, or walking with a friend, you build meaningful relationships. These social interactions provide emotional support, reduce feelings of isolation, and improve overall mental well-being. Furthermore, working out with others can motivate you to stay on track with your fitness goals, creating a positive feedback loop of improvement and encouragement.
Final Thoughts | Are the Benefits of Regular Exercise for Mental Health Worth it?
At Active Health Sport, we believe that mental and physical health are deeply interconnected. Regular exercise is one of the most effective ways to improve both your mind and body, offering benefits that go far beyond physical fitness. From reducing stress and anxiety to boosting mood and cognitive function, the mental health benefits of exercise are numerous and well-documented.
Whether you’re looking to relieve stress, improve your sleep, or simply boost your mood, exercise is a powerful tool that can help you achieve a more balanced, healthier, and happier life. Remember, it’s never too late to start! Begin with small steps, whether it’s a short walk, a yoga session, or a gym workout. As you incorporate more physical activity into your daily life, you’ll begin to experience the positive effects on both your body and mind.
How has regular exercise improved your mental health and overall well-being? We’d love to hear your stories, favorite workouts, or tips in the comments below! Whether it’s a unique routine that works for you or a question about how exercise can enhance mental health, feel free to share your thoughts or connect with us via email. We’re here to support your journey to a healthier mind and body!
You might also like…
- Why Mobility Matters More Than Muscle for CrossFit Progress
 In CrossFit culture, strength numbers often steal the spotlight: heavier deadlifts, faster WOD times, and bigger PRs. While muscle and power are essential, they are not the limiting factor for long-term CrossFit progress.… Read more: Why Mobility Matters More Than Muscle for CrossFit Progress
In CrossFit culture, strength numbers often steal the spotlight: heavier deadlifts, faster WOD times, and bigger PRs. While muscle and power are essential, they are not the limiting factor for long-term CrossFit progress.… Read more: Why Mobility Matters More Than Muscle for CrossFit Progress - Zone-2 Walking for CrossFit Athletes Explained
 In CrossFit, conditioning is often associated with intense, fast-paced WODs, high heart rates, and breathless finishes. While this intensity builds power and short-term fitness, it does not fully support aerobic efficiency, recovery capacity,… Read more: Zone-2 Walking for CrossFit Athletes Explained
In CrossFit, conditioning is often associated with intense, fast-paced WODs, high heart rates, and breathless finishes. While this intensity builds power and short-term fitness, it does not fully support aerobic efficiency, recovery capacity,… Read more: Zone-2 Walking for CrossFit Athletes Explained - How Low-Intensity Walking Restores the Nervous System
 CrossFit is designed to test physical limits. Heavy lifts, fast-paced metabolic conditioning, and complex gymnastic movements demand not only muscular strength but also significant nervous system output. While most athletes focus on muscle… Read more: How Low-Intensity Walking Restores the Nervous System
CrossFit is designed to test physical limits. Heavy lifts, fast-paced metabolic conditioning, and complex gymnastic movements demand not only muscular strength but also significant nervous system output. While most athletes focus on muscle… Read more: How Low-Intensity Walking Restores the Nervous System

Kait Amazra is the founder and lead writer of Active Health Sport. With over 25 years of experience in health, fitness, and wellness education, Kait combines professional expertise with a passion for helping people live stronger, healthier, and more balanced lives.
As a licensed health and fitness professional, Kait has worked alongside industry experts to deliver evidence-based insights on physical activity, nutrition, recovery, and holistic well-being. Through Active Health Sport, Kait’s mission is to make trusted, practical, and science-backed health information accessible to everyone, from beginners building new habits to athletes seeking peak performance.

Your blog helped me a lot.
Thank you for your sharing.